IV Fluids for Diarrhea and Vomiting: Dehydration Treatment
Diarrhea and vomiting strip the body of fluids within hours, leaving you weak, dizzy, and at risk of severe dehydration. While sipping water helps, it often isn’t enough, especially when frequent vomiting prevents you from keeping fluids down. That’s where IV therapy comes in.
IV fluids provide rapid rehydration therapy and also address electrolyte imbalance in the body.
How Diarrhea and Vomiting Lead to Dehydration
Severe diarrhea and frequent vomiting cause massive loss of water and plasma sodium, increasing the risk of hypernatraemic dehydration. Hypernatraemic dehydration is a condition where the body has too little water relative to its sodium.
This loss disrupts blood electrolyte levels and can also cause metabolic acidosis, where the body's acid-base balance is impaired. Without proper management, fluid buildup complications and hypovolemic shock, a life-threatening state due to reduced blood volume, can occur.
Common causes of diarrhea and vomiting include stomach viruses, food poisoning, or bacterial infections. In these conditions, the digestive system struggles to absorb fluids properly.
Without treatment, dehydration can worsen and affect your heart, kidneys, and circulatory system. This is especially true for dehydration from stomach flu, where fluid loss is rapid and ongoing.
Signs and Symptoms of Dehydration
Recognizing dehydration early is critical, especially when it stems from diarrhea or vomiting. The faster fluids are lost, the higher the risk of complications such as severe dehydration and metabolic acidosis (when there is too much acid in the body, causing the blood's pH to drop below normal).
Here are some key warning signs of dehydration:
- Dry mouth and constant thirst: When fluid reserves drop, the body sends thirst signals. A persistently dry mouth indicates that your fluid loss is outpacing your intake.
- Dark urine or reduced urination: Healthy hydration produces light-yellow urine. Dark urine or reduced urine output means the kidneys are conserving water to protect circulation. This is an early marker of worsening dehydration.
- Dizziness, fatigue, or weakness: With reduced blood volume, oxygen delivery to muscles and the brain drops. This can cause lightheadedness, exhaustion, and muscle weakness, particularly dangerous if combined with a stomach virus that keeps draining fluids.
- Rapid heartbeat and low blood pressure: These are red-flag signs that your circulation is under stress. They often indicate your body is entering hypovolemic shock, a life-threatening condition where blood volume drops dangerously low.
In more advanced cases, dehydration may also cause confusion, fainting, or difficulty staying awake, signs that you need to see a medical professional immediately.
Why Oral Rehydration Sometimes Falls Short

Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is often the first line of defense against dehydration from diarrhea and vomiting. Drinking water, electrolyte drinks like Ringer's lactate solution, or ORS solutions.
These drinks and solutions are specifically formulated to replace lost fluids and vital minerals like sodium chloride and potassium.
However, there are several instances where oral rehydration therapy falls short:
Severity of Dehydration
In situations of severe dehydration, oral fluid supplementation may not be effective or fast enough.
When fluid loss is rapid and large, the body needs faster replacement than the digestive system can handle. In such cases, rapid rehydration therapy via IV infusion is more reliable because it restores hydration directly and quickly.
Vomiting Limits Oral Intake
If vomiting is frequent, it’s difficult to keep fluids down. Every sip may be lost before absorption begins. This creates a cycle where the body cannot replace what it loses, making dehydration worse.
IV therapy bypasses the stomach entirely, ensuring fluids and electrolytes stay in the body.
Gastrointestinal Absorption Issues
Certain underlying conditions or severe infections might impair the gastrointestinal tract's ability to effectively absorb fluids.
This means that even if ORS solutions can be ingested, they may not be adequately absorbed, necessitating the use of IV fluids to ensure proper hydration and nutrient balance.
Unresponsiveness or Altered Consciousness
Severe dehydration can cause confusion, drowsiness, or even loss of consciousness. In this state, drinking fluids is unsafe and often impossible. It risks choking or aspiration if the patient cannot swallow properly.
In these scenarios, IV therapy is critical as it allows healthcare providers to bypass the digestive system entirely and directly administer necessary fluids and electrolytes into the bloodstream.
What’s in an IV for Dehydration?
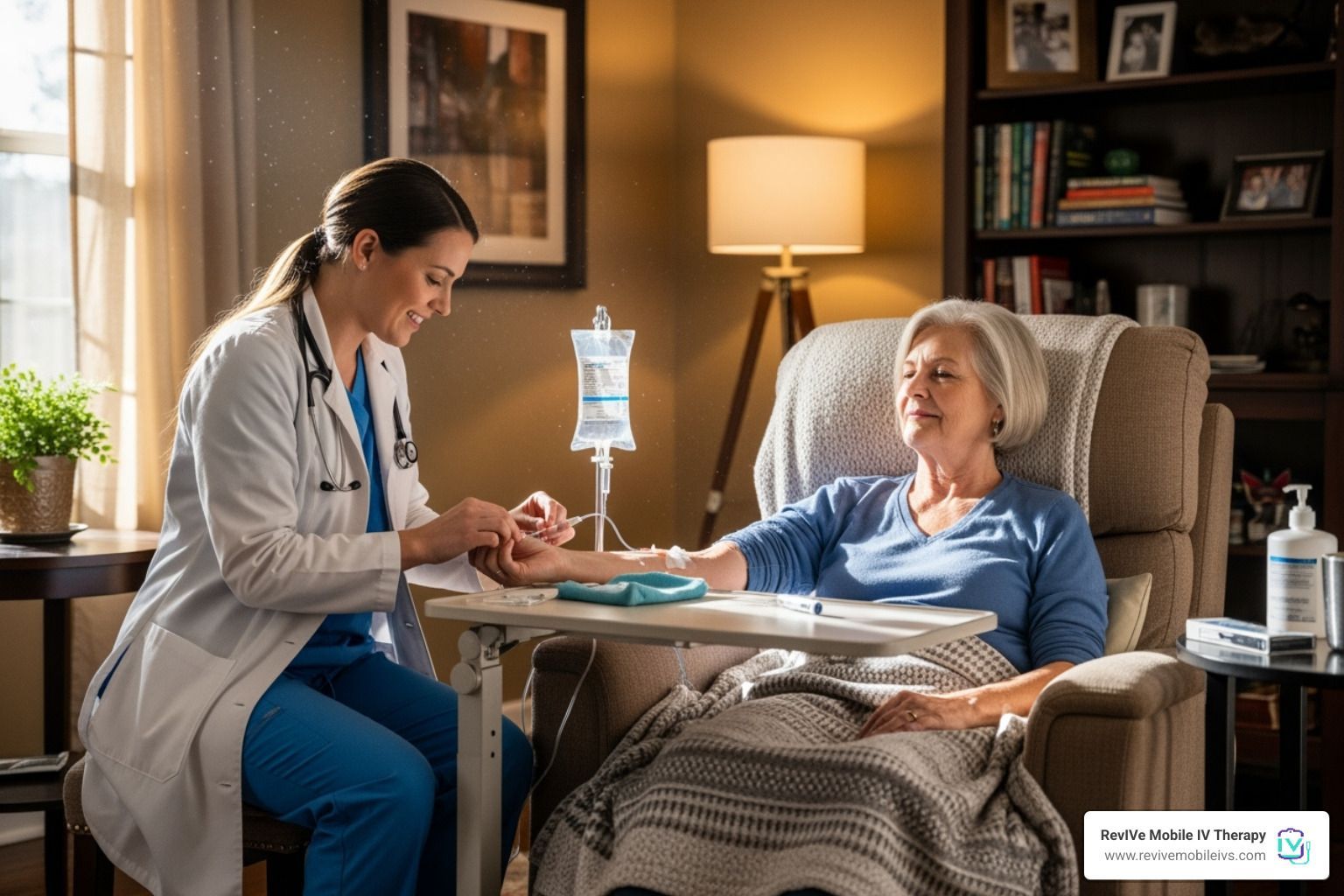

IV fluids for dehydration are carefully formulated to replace the fluids the body loses. They contain more than just water. Each component plays a unique role in restoring balance and helping you recover faster.
- Saline solution: The base of most IV drips is saline. These solutions are designed to match the body's natural fluid balance, making them ideal for rapidly replenishing lost fluids without significantly altering the electrolyte balance.
- Electrolytes: Electrolytes are minerals that control nerve signals, muscle contractions, and hydration. Sodium restores balance in the blood. Potassium supports muscle and heart function. Magnesium eases cramps and supports energy production. Together, they prevent complications like irregular heartbeat or muscle weakness.
- Vitamins: Many dehydration drips include vitamins for added recovery. B-complex vitamins support energy, focus, and metabolism. Vitamin C boosts the immune system and helps repair tissues.
- Other nutrients: In some cases, providers may add zinc or calcium. These help with immune defense and bone strength. Add-ons are tailored to your needs and overall health.
Some drip infusions include dextrose solutions, a simple sugar solution. Dextrose provides quick energy when the body is weakened by diarrhea or vomiting. It helps stabilize blood sugar, support recovery, and restore strength faster than hydration alone.
These combinations in IV drips help tackle the imbalance of electrolytes, stabilize the circulatory system, and support the digestive system during recovery. The result is faster relief and better overall balance.
Benefits of IV Fluids for Diarrhea and Vomiting
IV fluids offer several important advantages when addressing dehydration caused by severe vomiting and diarrhea:
- Rapid rehydration: Fluids go directly into the bloodstream. This allows faster absorption than when oral rehydration therapy is used.
- Electrolyte balance: Diarrhea and vomiting strip the body of sodium chloride, potassium, and magnesium. IV fluids quickly replace these electrolytes.
- Reduced nausea: Many dehydration drips include anti-nausea medication when prescribed by a provider. This eases symptoms and helps patients feel comfortable again.
- Support for digestion: Rehydration helps the digestive system recover. Balanced fluids and electrolytes reduce stomach irritation and improve nutrient absorption after illness.
- Energy and recovery: Optional vitamins, like B-complex and Vitamin C, support energy production and tissue repair.
- Kidney protection: Adequate fluids prevent strain on the kidneys. This reduces the risk of kidney injury or complications during severe dehydration.
- Customizable Relief: IV fluids can be adjusted for each patient’s needs by medical professionals. Whether caused by food poisoning, a stomach bug, or another illness, treatment is tailored by a licensed provider.
In addition, the delivery of fluids happens in a controlled manner, allowing for precise dosages and even adjustable delivery depending on patient needs.
Safety Considerations and Limitations
While IV fluids are highly effective, they should always be administered by a qualified medical professional. Risks include:
- Allergic reactions or sensitivities to additives in the fluids.
- Rare reactions to ingredients if the mix isn’t tailored properly.
- Fluid buildup in patients with kidney or heart conditions.
- Potential complications include worsening metabolic acidosis if the wrong balance of sodium chloride and electrolytes is used.
Also, the medical professional should clean the area around the vein with alcohol before the needle is placed. This prevents infections from the drip devices, keeping the procedure safe.
At Revive Mobile IVs, treatments are delivered by licensed providers who follow strict safety protocols, ensuring IV therapy is both effective and risk-free.
When to Seek Further Medical Attention
IV fluids help with moderate dehydration, but some cases need more urgent care. Seek immediate help if you have severe abdominal pain, bloody stool, or vomiting that won’t stop. Here, you need rapid rehydration therapy and further care from a medical professional.
OTC medications, ORS solutions, and other oral fluid supplementation may ease mild cases, but persistent or severe symptoms require professional intervention.
People with chronic medical conditions like kidney failure or liver problems should use IV therapy under strict professional supervision. Always consult a licensed healthcare provider before treatment.
IV hydration is most effective in dealing with stomach flu symptoms when administered under professional care. By recognizing when to seek medical attention and choosing safe rehydration methods, you can support your body’s recovery and overall wellness with confidence.